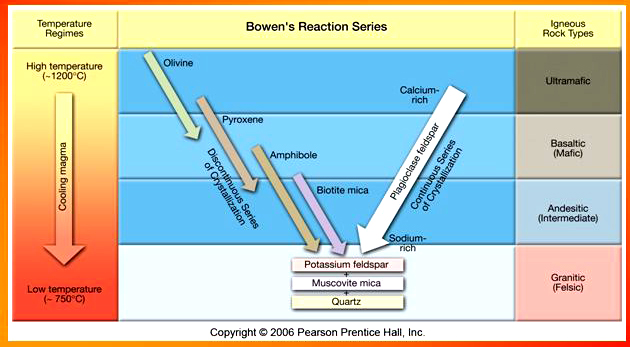
Bowen's reaction series describes __1__ . The first minerals to crystallize are __2__ , hence the residual melt will __3__ . If the early-formed minerals remain in contact with the melt, at lower temperatures they will react with the silica in the melt to form new minerals. Reactions continue until all of the silica in the melt is used-up or until biotite forms and the remaining melt crystallizes. The resulting rock will have a __4__ . However, if the early formed minerals are separated from the residual melt (e.g. crystal settling or "squeezing"), then they will not be able to react with the melt, __5__occurs, and __6__ will be formed. The early-formed minerals will form a rock with a lower concentration of silica than that of the parent magma, but the residual melt will eventually crystallize to form a rock with a higher concentration of silica than that of the parent magma. Thus, rocks of different compositions can be formed from the same parent magma.
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |